what is service level agreement
The full form of SLA is Service Level Agreement. This is called service level agreement in Hindi. It is a document that describes the quality and performance of a service; What a service provider promises to deliver to customers. It addresses several areas related to service performance such as performance display criteria, customer support, guarantee and warranty.
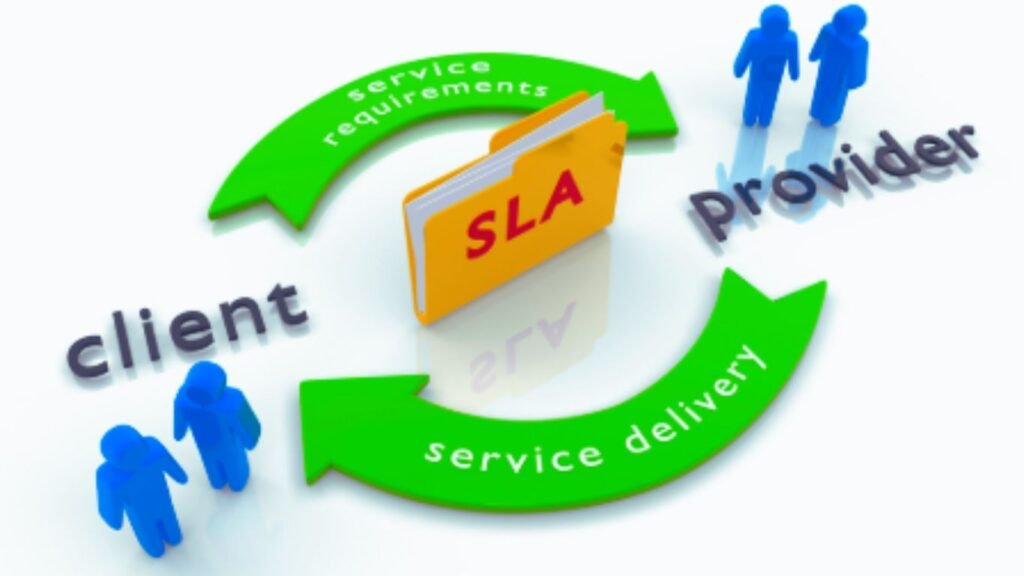
An SLA is a key component of the legal contract between a service provider and a consumer, as it also describes penalties and remedial actions if the service provider does not provide the service described in the SLA.
Its agreement is prepared in simple language so that the customer can understand it clearly. This may include technical terms to define the performance of the service. SLA usually Telecom Used in companies, internet service providers and IT Service Providers which comes under SLA; A typical example of an SLA is a data center service-level agreement. This SLA includes an uptime guarantee that indicates the percentage of time the system is available. Anything less than 99.99% uptime should not be considered acceptable for modern enterprise-level data centers. Another typical example of an SLA is an Internet service provider service-level agreement. Uptime guarantee in this SLA but it will also define packet delivery expectations and latency. Packet delivery refers to the percentage of data packets that are received compared to the total number of data packets sent. is the amount of time it takes for a packet to travel between the client and the server.
requires a Service-Level Agreement
SLAs originated with network service providers, but are now widely used in IT related areas. Some examples of industries that establish SLAs include IT service providers and managed service providers, as well as cloud Computing and Internet service providers are included. Corporate IT organizations, particularly those that have adopted IT service management, enter into SLAs with their in-house customers along with users from other departments within the enterprise. An IT department creates an SLA so that its services can be compared, justified, and perhaps measured, with those of outsourcing vendors.
On the basis of which metrics is the performance of SLA determined
SLA Performance : SLAs establish customer expectations regarding service provider performance and quality in several ways. Some metrics that may specify SLAs include-
1. Availability and Uptime Percentage The time the services are up and running and accessible to the customer. Typically tracked per month and reported per month or billing cycle.
2. Specific Performance Benchmarks Actual performance is measured against these benchmarks from time to time. Will be compared to.
3. Service Provider Response Time – The time it takes for a service provider to respond to a customer’s issue or request. A large service provider provides a service to respond to customer inquiries. Can operate a desk.
4. Resolution time – The time taken by the service provider to resolve the issue after it is resolved.
5. Abandonment rate – The percentage of customers who abandon queued calls while waiting for an answer.
6. Business results to influence the business performance of service providers. Using KPIs to determine approach.
7. Error Rate – The percentage of errors in a service, such as coding errors and timeouts.
8. First-Call Resolution – The percentage of incoming customer calls that are resolved without the need to call the help desk.
different types of SLA
Types of SLAs : A service level agreement (SLA) is a contract between a business and its customer, outlining the details that both parties have agreed to in the transaction. There are many types of SLAS that an organization may use.
depend on important aspects. Three basic types of SLAs –
1. Service based SLA-This SLA is a contract that covers the same type of service for all its customers. Because service is limited to an unchangeable standard. It is more simple and convenient for the seller. For example, using a service-based agreement regarding an IT helpdesk would mean that the same service is valid for all end-users who sign the service-based SLA.
2. Customer based SLA-This type of agreement is used for individual customers and covers all relevant services. Which the customer requires, while only one contract can be availed. It contains details about the type and quality of service that has been agreed. For example, a voice call in a telecommunications service. Messaging and Internet services are included, but all under one contract.
3. Multilevel SLA – This agreement is customized as per the needs of the end user company. This allows the user to integrate multiple conditions into a single system to create a more suitable service.
SLA connects the Service and the Customer and also applies at the corporate level for all users in an organization. Multilevel SLAs avoid duplication between multiple agreements and the inefficiencies that can occur when multiple It becomes possible to integrate situations.
key components of SLA
The key components of Service Level Agreement are as follows-
1. Agreement overview – This first section sets out the basics of the agreement, including the parties involved, the commencement date and a general introduction to the e-services provided.
2. Description of services SLA requires a detailed description of each service under all possible circumstances, including turnaround times. Service definitions should include how services are delivered. What maintenance services are offered? What are the hours of operation, where dependencies exist, an outline of procedures and a list of all technology and applications used.
3. Exclusions – Specific services that are not provided should also be clearly defined to avoid confusion and eliminate room for assumptions from other parties.
4. Service performance-Performance measure metrics and performance levels are defined. The customer and service provider must agree on a list of metrics they will use to measure the provider’s service levels.
5. Redressing – Compensation or payment should be defined if a provider has not met its SLA.
6. Stakeholders – The agreement clearly defines the parties involved and establishes their responsibilities.
7. Security- All the security measures taken by the service provider are defined. Typically, this involves drafting and agreeing on antipoaching, IT security and nondisclosure agreements.
8. Risk management and disaster recovery – Risk management procedures and a disaster recovery plan are established and clearly communicated.
9. Service tracking and reporting – This section defines the reporting structure, tracking intervals, and stakeholders involved in the agreement.
10. Periodic review and change processes – SLA All established key performance indicators (KPIs) should be reviewed regularly. This process is defined as the appropriate process for making change.
11. Termination process – The SLA should define the circumstances under which the agreement can or will be terminated. The period of notice from both sides shall also be established.
12. Signatures – Finally, all stakeholders and authorized participants on both sides should sign the document to show their approval to every detail and process.
thanks for reading me blog please leave me comments.
