Definition of atmosphere
The wide expanse of air that surrounds the Earth is called atmosphere. The study of the upper layer of the atmosphere is called Aerology and the study of the lower layer is called Meteorology. Air is an integral part of the Earth’s mass and 99% of its total mass is located 32 km above the Earth’s surface. Situated at a height of.
Some important gases found in the atmosphere
1. Nitrogen: Percentage of this gas Volume is greater than all gases. Due to the presence of nitrogen, air pressure, strength of winds and reflection of light are felt. This gas has no colour, smell or taste. The biggest advantage of nitrogen is that it prevents objects from burning rapidly. If there was no nitrogen in the atmosphere, it would have been difficult to control the fire. Proteins are produced in plants from nitrogen, which is the main component of food. Km. It extends up to a height of.
2. Oxygen: It works with other substances to cause burning. We cannot burn fuel in the absence of oxygen. Therefore it is the main source of energy. This gas extends up to a height of 64 kilometers in the atmosphere, but its quantity reduces significantly after going above 16 kilometers. At an altitude of 120 km the amount of oxygen becomes negligible.
3. Carbon-dioxide: It is the heaviest gas and hence it is found in the lowest layer. Most of its extension is up to a height of 32 km. Well it is 90 mm. It is found up to a height of. This gas is permeable to radiation coming from the Sun and impermeable to radiation reflected from the Earth. Therefore, it is responsible for the glass house effect and keeps the lower layer of the atmosphere warm. The volume of other gases is stable in the atmosphere, whereas the volume of carbon dioxide has been continuously increasing in the last few decades, mainly due to the burning of fossil fuels.
4.Ozone: This gas is a special form of oxygen. It is found in very small quantities in the atmosphere only at high altitudes. It absorbs some part of the strong ultraviolet radiations coming from the Sun. It is concentrated at an altitude of 10 to 50 km. Due to reduction in the amount of ozone gas in the atmosphere, ultraviolet radiation from the Sun can reach the Earth in large quantities and spread terrible diseases like cancer.
5.Water Vapor: Water vapor is the most variable and unevenly distributed gas in the atmosphere. It decreases with height. It is 90 km. It is found only up to a height of. of the atmosphere 90% of all water vapor is within 8 km. Is limited to a height of. Due to its condensation, clouds, rain, fog, dew, frost, snow etc. are formed. Different types of storms get energy from water vapor only. Water vapor absorbs some part of the insolation coming from the Sun and stores the heat radiated by the Earth. In this way it works as a blanket, due to which the earth can neither become too hot nor too cold. Rain occurs due to condensation of water vapor. The stability of the atmosphere is also controlled by water vapor.
CO₂ and water vapor are responsible for maintaining the earth’s temperature.
Composition of the atmosphere:
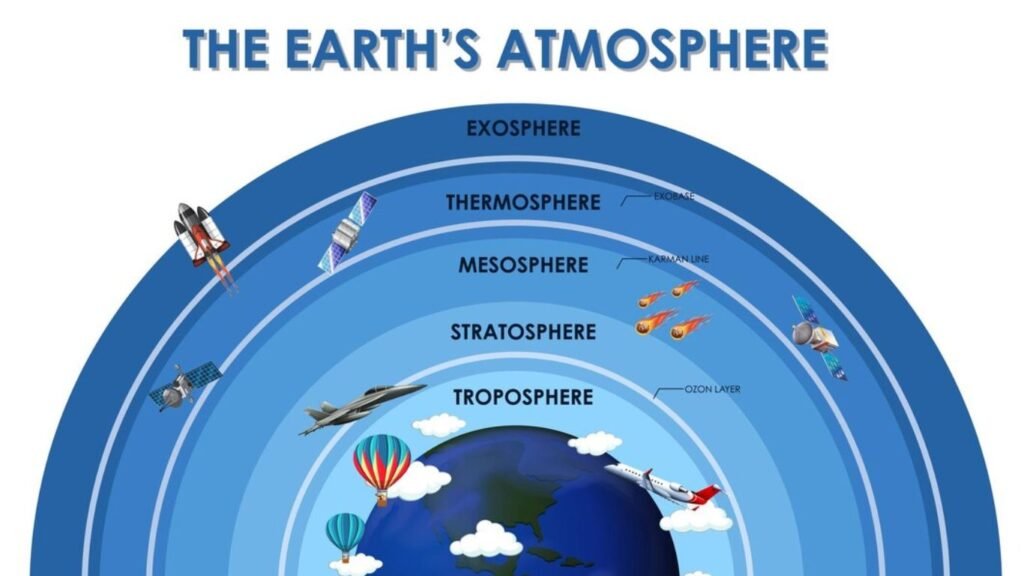
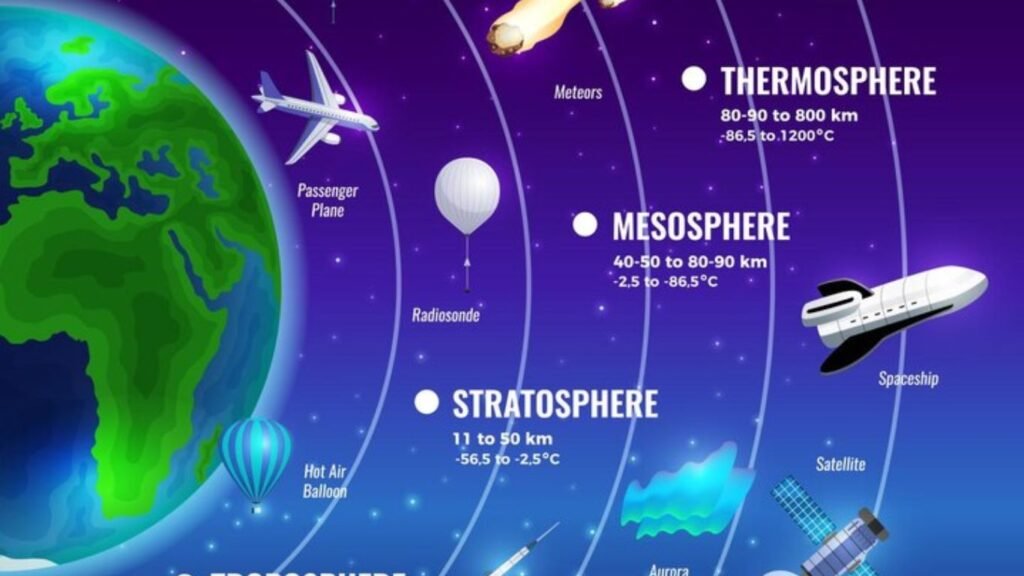
The atmosphere is divided into the following layers
1. Troposphere: This is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. Its height is about 18 km from the surface. Is. Its height at the poles is 8 km. and about 18 km on the equator. occurs. The rate of fall of temperature in the troposphere is 1°C per 165 meter height or 1 km. It is 6.4°C at altitude. All the main atmospheric phenomena like clouds, storms and rains occur in this zone. This zone is called convection zone, because convection currents are limited to the limits of this zone. This region is also called the lower region. This is the most important layer for biological activity. The part separating the troposphere and stratosphere is called the troposphere. The air temperature in the troposphere above the equator is -80°C and above the pole is 45°C.
1.Stratosphere: Stratosphere 50 km. Is up to a height of. The thickness of the stratosphere is greatest at the poles, sometimes disappearing at the equator. There are no seasonal events like storm, thunder, lightning, dust particles and water vapor etc. in this. Ideal conditions for flying airplanes are found in this region. Sometimes a special type of clouds are formed in this region, which are called Mother of pearl clouds. An important characteristic of the stratosphere is that it contains a layer of ozone gas, which absorbs ultraviolet rays coming from the Sun. That is why it is called the earth’s protective shield. The gas that destroys the ozone layer is CFC (Chloro-fluoro-carbon), which comes out from air conditioners, refrigerators etc.
3. Mesosphere: Mesosphere, 80 km just above the stratosphere. It extends up to a height of. In this layer also the temperature starts decreasing with height and after 80 km. After reaching a height of -100°C. The upper layer of the middle layer is called the central boundary.
4. Ionosphere: The ionosphere is 80 km above the mesosphere. 400 km from. Located between. Electrically charged particles are found in it, which are called ions and that is why it is known as ionosphere. The temperature starts increasing with increasing altitude in the ionosphere. In this layer, long radio waves are reflected from the D-layer located at the bottom and short radio waves are reflected from the E, E₂ and F, F,₂ layers, as a result of which the facilities of radio, television, telephone and radar etc. are available on the earth. Communication satellites are located in this region.
