African ancestors of humans
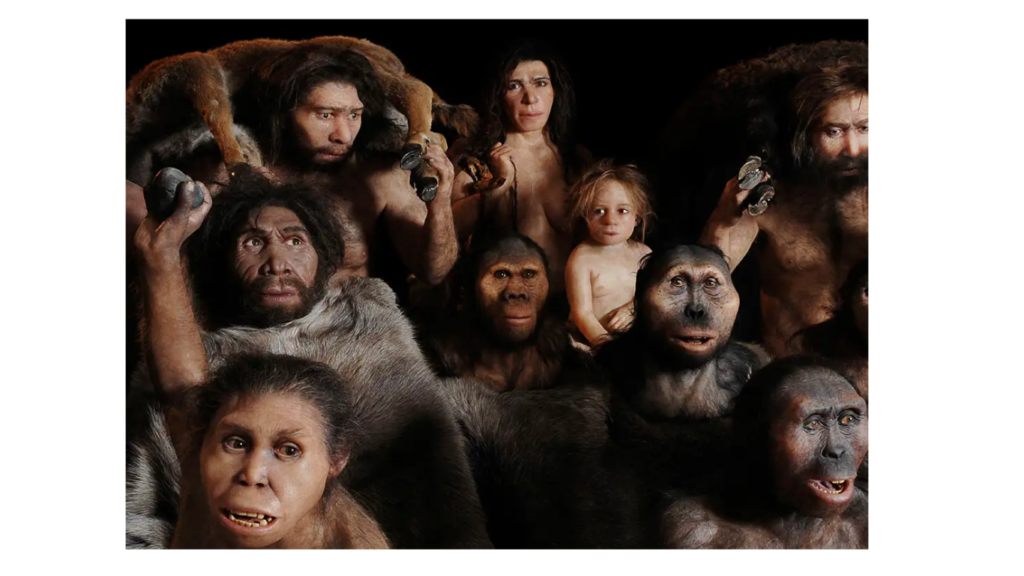

The earth is 4600 million years old. There are four stages of development of the earth’s crust and the fourth stage is known as ‘Quatrbha’. Green is 1 of the earth. It is divided into two eras, called Navayuga (Ice Age) and Abhinav Yuga (Post-Ice Age). Its first part B.C. From 20 lakh BC It is till 12,000 years and the second part is in B.C. It is believed to be from 12,000 to today. Although life on Earth began 3500 million years ago. It was limited to plants and animals for several million centuries. Humans appeared on Earth in the pre-ice age and early ice age. A variety of humans called hominids lived in southern and eastern Africa about 6 million years ago. The earliest known human beings evolved about 30 million years ago. The birth of a creature called Australopithecus was the most important event in the evolution of human life. Australopithecus is a word that originated in Latin and means a southern ape-like creature. This species had characteristics of both apes and humans and evolved between about 5.5 million and 1.5 million years ago. These creatures had two legs and a pitcher-shaped stomach; the size of their brain was approximately 400 cubic centimeters. Some elements of other living creatures called Homo or humans were found in Australopithecus. Man represents the evolution of the hominid line and Australopithecus represented the last stage of pre-human hominid. This is the reason why this species is also called proto-human.
first significant animal was Homo or humans, Homo habilis, which lived in eastern and southern Africa between 20-15 million years ago. Homo Habilis means a normal or slightly skilled human being. This first real man broke stone into pieces and then turned it into tools. Made sharp for various uses. Near the site of Homo Habilis bones Fragmentary pieces of stones are also found. The size of the brain of this creature is about 500-700 It was of these centimeters. The second important event was the discovery of Homo erectus 18 to 16 lakh years ago. Homo erectus means an erect or erect soul. Its skull was quite strong, its brain size was 800-1200 cubic centimeters.
New types of stone tools have been found with Homo erectus. Among these, the ax is considered to be the most special. It is believed that Homo erectus people invented the method of making and using fire, which allowed them to stay warm in cold climates and also remain safe from wild animals. Unlike Homo habilis, Homo erectus traveled long distances. Their remains have been found not only in Africa but also in China, South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The third event is the emergence of Homo Sapiens. Homo sapiens means intelligent person. Our own species evolved from Homo sapiens. It looks like Neanderthal man. Which were found in Western Germany about 230 to 30 thousand years ago. Its body and head were very small but its brain measured 1200 to 1800 cubic centimeters. This species probably evolved in Europe, but Neanderthals have also been found in the Near East and elsewhere in the Old World.
Fully developed modern humans, Homo sapiens sapiens, were found in southern Africa during the late Stone Age, about 115,000 years ago. Which was called the Upper Palaeolithic Age. Compared to other hominid species, its forehead was larger and its bones were thinner. Modern humans originally made various stone tools for various tasks, but it is not clear whether they were physically capable of speaking. Until recently it was thought that the language originated in B.C. It originated around 35,000 BC but is now dated to B.C. It is considered to be up to 50,000. However, Homo sapiens sapiens had a large round brain measuring 1200–2000 cubic centimeters. This enabled modern man to function more effectively and enable him to adapt to his environment.
early humans of India

Only a few fossils related to human development have been found in this subcontinent. However, some of the oldest skull fossils have been found in the Shivalik Hills spanning India and Pakistan. These skulls have been found on sandstone in Potwar Plateau and Punjab province of Pakistan. These skulls are called Ramapidhikas and Shivapidhikas. They are believed to have hominid characteristics, although they display ape-like features. Ramapithecus was female but both belonged to the same group. from this group Their related ancestors were found in Egypt 10 million or 10 million years ago. This could be a basis for dating Ramapithecus and Shivapithecus but these skulls are considered to be 22 lakh years old. This does not in any way suggest that this species spread to other parts of the subcontinent. It appears that the development of Shivalik range hominids stopped in the subcontinent and ultimately this species became extinct.
Yet in 1982, a nearly complete hominid skull was discovered in the central valley of the Narmada at Hathnora, Madhya Pradesh. This fossil skull was called Homo erectus or erect man but is now recognized as ancient Homo sapiens.
Till now, remains of Homo Sapiens have not been found anywhere in this subcontinent. However, remains of a fully modern human being, Homo sapiens sapiens, have been found in Sri Lanka. This place is called Fahiyan and the fossils found around it are 34 thousand years old. It was a hunting and nomadic lifestyle found in Sri Lanka in the late New Age and pre-New Age. Fahiyan Cave is the oldest and Upper Stone Age site in the Indian subcontinent. The remains found here are about 31 thousand years old. Modern humans are believed to be 34 thousand years old. After all the studies, it seems that the oldest modern humans reached India about 50 thousand years ago through coastal migration from Africa to the south. They did not come from the North.
Stages of Paleolithic Age

The Palaeolithic Age in India is divided into three phases according to the stone tools used by people and the nature of climatic changes. The first phase is called the Ancient or Lower Palaeolithic Age, the second is called the Middle Palaeolithic Age and the third is called the Upper Palaeolithic Age. Until sufficient information is obtained about Bori artefacts, the first phase, from 6 lakhs to Between 15 lakhs, the second B.C. 1.5 lakh to B.C. Between 35 thousand and 3rd BC. 35 thousand BC It can be between Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 10,000. Although B.C. Tools belonging to both the Middle and Upper Palaeolithic era, between 35 thousand and 15 thousand BC, have been found in the Deccan Plateau.
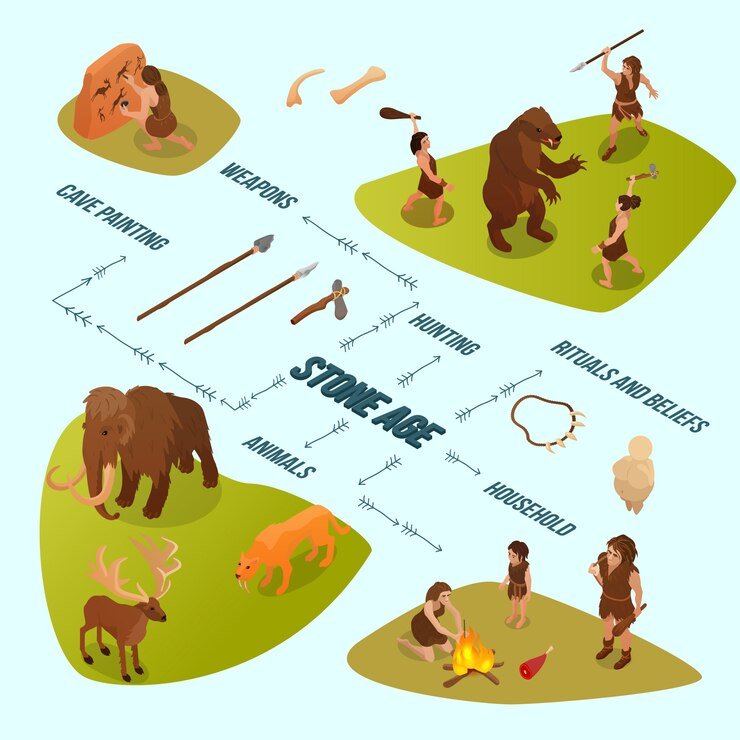
The Lower Palaeolithic Age, or Early Palaeolithic Age, represents the maximum part of the Ice Age. The ancient Palaeolithic age began in Africa about 20 lakh years ago but in India it is not more than 6 lakh years old. This date has been determined for Bori in Maharashtra and the site is considered to be the oldest Lower Palaeolithic site. People used hand tools like axes, maces and knives. Axes found in India are from Western Asia, Europe and Africa are similar. Stone tools were mainly used for cutting, digging and tanning. Ancient Palaeolithic sites have been found in the Sohan or Son river valley of Punjab, now in Pakistan. Many sites have been found in Kashmir and the Thar Desert. Lower Palaeolithic tools have been found in the desert area of Belan in Uttar Pradesh and Didwana in Rajasthan. Tools not only of Lower Palaeolithic but also of Middle and Upper Palaeolithic era have been found from Didwana. More than 2000 tools have been found in Chirki-Nevasa in Maharashtra and similar tools have been found in many places in the south also. Nagarjuna Konda is an important site in Andhra Pradesh and the caves and rock shelters of Bhimbetka near Bhopal also show the characteristics of the Lower Palaeolithic Age. The rock shelters were used as camps for humans depending on the weather. Hand axes have been found in deposits of the Second Himalayan interglacial period, when the climate became less humid. People in the Lower Stone Age were mainly food gatherers. They played small game and depended on hunting fish and birds. The Ancient or Lower Stone Age in India can also be associated with the people of the Homo Sapiens group.
The works of the Middle Palaeolithic period were mainly based on stone flakes or small fragments, found in different parts of India with regional variations. The main tools were blades, spears, augers and scrapers, all made of stone flakes. The geographical areas of the Middle Palaeolithic site generally correspond to the Lower Palaeolithic. Artefacts of this era are found in many places south of the Narmada and Tungabhadra rivers. The Belan Valley (Uttar Pradesh), located in the foothills of the Vindhyas, is rich in stone tools and animal fossils including those of cattle, deer, etc. These belong to both the Lower and Middle Stone Age.
Middle Stone Age: hunters and herders
B.C. The Upper Paleolithic ended with the end of the Ice Age around 10,000 AD. As we know that in the global context, the Ice Age after the New Age (Pleistocene) coincided with the Palaeolithic Age, from 2 million years ago to BC. Lasted up to 12,000. And when it ended the climate became hot and rainy. Climate change brought changes in fauna and flora. Man took advantage of adequate rainfall, dense vegetation and forests. There have been no major changes in climate changes since then.
B.C. An intermediate phase in the Stone Age culture began in 9000. Which is called the Middle Stone Age. It is known as a transitional stage between the Palaeolithic and the Neolithic or New Stone Age. Middle Stone Age people hunted, fished, and gathered food. In the later stage they also started animal husbandry. In the first three works the Paleolithic lifestyle continued. Whereas at the end Neolithic culture developed. In this way, the Middle Stone Age became a transition period and also reflects the first phase of the Middle Stone Age with a livelihood based on animal husbandry. The special tools of the Middle Stone Age are microliths or small ones. Mesolithic sites are also found in Rajasthan, southern Uttar Pradesh, central and eastern India and south of the Krishna River. Among them, good excavations have been done in Bagor, Rajasthan. Its specialty is small tools and the residents here earned their livelihood through hunting and animal husbandry. B.C. Five Millennium to 5000 BC Such places continued to exist till. The earliest evidence of animal husbandry in the Indian subcontinent is found in Adamgarh in Madhya Pradesh and Bagor in Rajasthan. This B.C. Could be around Rs 5000. Through study it is revealed that in Rajasthan B.C. Cultivation is estimated to have occurred around 7000-6000 AD, which is before the formation of salt water lakes and the collection of sambar.
Till now, only a few discoveries of the Middle Stone Age have been scientifically dated. Mesolithic culture BC From 9000 BC It remained important till 4000 and undoubtedly paved the way for the rise of Neolithic culture.
Art in the paleolithic age
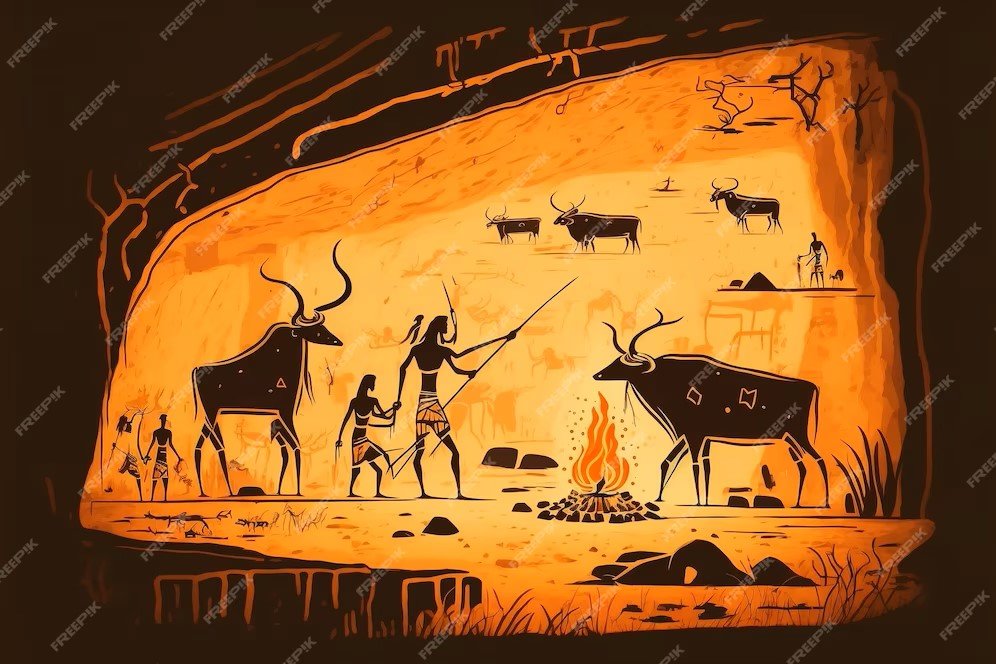

People of the Palaeolithic and Mesolithic ages practiced painting. Prehistoric art is visible in many places but Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh is a stunning site. Located in the Vindhya Mountains, 45 kilometers south of Bhopal, 10 square kilometers There are more than 500 painted rock shelters in the area. Rock paintings in Bhimbetka range from the Upper Palaeolithic to the Middle Palaeolithic era and in some series also depict the present day. However a large number of rock shelters have been associated with Middle Stone-Age works. These depict many birds, animals and humans and obviously most of the birds and animals present in these paintings were hunted for subsistence. Birds sitting on grains are not in the early paintings. These images clearly relate to the hunting/gathering economy.
Why did people of the Upper Palaeolithic Age do art? It is argued that they did this for the sake of art. However, this argument seems very artificial in view of the early stage of human history. It is also said that they adopted art and these practices to overcome social conflict. It may apply to complex social structures that suffer from severe social discrimination. Such was the situation in the Upper Palaeolithic society. Various wild animals were depicted to ensure people had control over them in any case as hunting was their main means of livelihood. Although we find some images of men and women, various types of animals can be seen here again and again. The practice of animal depiction in the context of hunting was real. In the context of Harappa, animal paintings become traditional. Although the people depended mainly on agriculture, Harappan seals depict images of animals.
early human organization
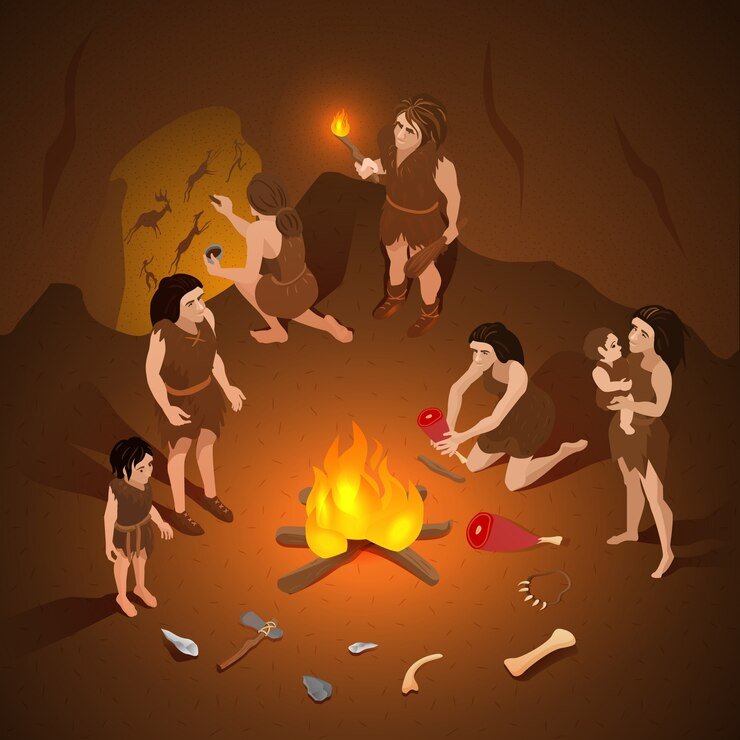

How did humans organize socially? It is not clear whether he lived in any group or pre-group society. A group would have been formed for hunting and the maximum number could have been 25. There could be an alliance between different groups for mutual help and the number of such a large group could not exceed 500. Some rituals would have been organized to confirm these alliances. Eventually, this group transformed into a heterogeneous marital group called a clan in the Neolithic period. Members of a clan always married outside the clan but these clans had established relationships for mutual aid. In the Upper Paleolithic stage, members of a group used to hunt and collect food in a society and share it among themselves. The formation of bands or groups of bands may have been facilitated by the use of language that developed in the Upper Palaeolithic, and communication may have played an important role in people living together.
Please leave me comments
