service models of Cloud Computing
The service models of cloud computing are also called SPI (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) model. It has three layers. The topmost layer has SaaS, the second layer has PaaS and the lowest layer has IaaS model.
1. SaaS: Its full name is software as a service. It is a distribution network that makes software applications (such as browsers) available on the Internet as a service to customers.
In SaaS, customer data is completely secure and even if there is a glitch in the system, the data remains safe.
Examples of SaaS applications – google apps, office 365 etc.
2. PaaS- The full name of PaaS is platform as a service. It is a service provider that provides a platform to the customer in which he can easily create, manage and deliver software applications.
That is, PaaS provides a platform in which such tools are provided to the customer so that he can easily develop, customize and test the application.
Example-Google App Engine, Amazon Web Services etc.
3. IaaS- Its full name is infrastructure as a service. This is a service model in which hardware, networking and storage services are provided to the customer in a cloud environment.
In this model, it is the responsibility of the customer to update the software applications and operating systems that are installed by the customer.
Example- Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure etc
SaaS (Software as a Service):

Software as a Service is a distribution model that makes software applications (such as browsers) available on the Internet as a service to customers. A SaaS application is run on the servers of a SaaS provider and sometimes a SaaS application is Also called hosted application.
Software as a service (SaaS) allows users to connect to and use cloud-based applications over the Internet. Common examples are email, calendaring, and Office tools (e.g. Microsoft Office 365).
“Service” and “Cloud” mean in the context of SaaS
Meaning of “Service” in the context of SaaS Consider the difference between valet parking and rented parking spots. Valet parking is a service while a parking spot is a product, even though both provide the same benefit to the customer. A place to leave your car. Traditionally. Software vendors sell their software as products to users.
In the SaaS model they actively provide and maintain the software to their users through the cloud. They host and maintain the databases and code needed to run the applications and they run the applications on their servers. Thus SaaS is more like a service than a product.
“Cloud” in the context of SaaS means- “Cloud” refers to remote web servers in various web centers that host the database and run application code. Cloud providers deliver their services to customers or end users through the Internet.
advantages and disadvantages of SaaS (Software-as-a-Service).
Benefits of SaaS
1. Gain access to sophisticated applications – To provide a SaaS app to users, you do not need to purchase, install, update any hardware, middleware, or software. Or does not need to be maintained.
2. Pay only for what you use – You also save money because the SaaS service automatically scales up and down according to usage levels.
3. Use free client software – Users can run most SaaS apps from their web browser without the need to download and install any software. However, some apps require plugins.
4. Mobilize your workforce easily – SaaS your workforce “Jutana” makes it easy because users can access SaaS apps and data from any Internet-connected computer or mobile device. You don’t need to worry about developing apps to run on different types of computers and devices because the service provider has already done that. Additionally, there is no need to bring special expertise to manage the security issues inherent in your mobile computing.
5. Access app data from anywhere – With data stored in the cloud, users can access their information from any Internet-connected computer or mobile device and when app data is stored in the cloud So no data is lost if the user’s computer or device fails.
Disadvantages of SaaS
1. The need for stronger access control – The increased accessibility of SaaS applications also means that verifying user identity and controlling access levels becomes very important. With SaaS, organizational assets are no longer kept within an internal network isolated from the outside world.
2. Vendor lock-in – A business may become overly dependent on a SaaS application provider. If an organization’s entire database is stored in an old application, it is time-consuming and expensive to migrate it to the new application.
3. Security and Compliance for Enterprises With SaaS applications, the responsibility for securing physical applications and their data moves from internal IT teams to external SaaS providers. For small to medium-sized businesses, this is less of a disadvantage, as larger cloud providers typically have more resources to maintain strong security.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)

The full name of PaaS is Platform as a Service. It is a service provider that provides a Provides a platform through which one can easily create, manage and deliver software applications. PaaS is also commonly called middleware because it is a service model between SaaS and LaaS. PaaS (Platform as a Service) is a cloud computing model where a third party provider delivers hardware and software tools to users over the Internet. Generally, these tools are required for application development.
A PaaS provider hosts the hardware and software on its own infrastructure. As a result, PaaS prevents developers from having to install in-house hardware and software to develop or run a new application.
Other PaaS services include-
1. Development tome support
2. Application Design and Development
3. Application Testing and Deploy
4. Web service integration
5. Subana Security
6. Integration of Database
advantages and disadvantages of PaaS (Platform as a Service).
Benefits of PaaS
The main advantage of PaaS is simplicity and convenience for users. The PaaS provider will supply a range of infrastructure and other IT services that users can access anywhere through a web browser. Service availability or flexibility, however, can be a concern with PaaS. If a provider experiences a service outage or other infrastructure disruption it can adversely impact customers and result in lost productivity. However PaaS providers will typically offer relatively high volatility.
Disadvantages of PaaS
vvendor-lock-in is a common concern because users cannot easily transfer multiple services and data in one PaaS product to another competitor product.
For example, if a PaaS provider stops supporting a certain programming language or opts to use a different set of disruption tools, the impact on users can be difficult and disruptive.
Many PaaS products are tailored for software development. These platforms offer compute and storage infrastructure as well as text editing, version management, compiling and testing services that help developers create new software quickly and efficiently.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)

It is a service model in which hardware, networking and storage services are provided to the customer in a cloud environment. In this model, it is the responsibility of the customer to update the software applications and operating systems that are installed by the customer. In this type of service, the computing power, storage, software, network power and all other control of the cloud is available to the user. Is near. This service is basically used for business. The biggest example of this is VPS water Virtual private server.
This part refers to the architecture of infrastructure as a service.
1. Service Provider Cloud-The client uses a virtualized environment that provides service over the Internet. Can also be called as providing infrastructure. They have been given such components to build their own IT platforms. Cloud is flexible because users access IaaS anytime and from anywhere Could. The only requirement is an internet connection.
2. Hardware-The place where data is stored which can also be known as infrastructure or hardware. It is designed to be trusted and secure where the data is stored. It includes Virtual Server Raas, Network Many services like connection, bandwidth, IP address and load balancers are included.
3. Servers – Servers are maintained by the cloud providers and are completely managed by them. These servers and networks are distributed across multiple data centers. These data centers are secured by cloud providers.
benefits of IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
1. Protection and Recovery- Protection and recovery of data is an important aspect. It can also be seen that continuity and disaster recovery are costly to achieve. Due to this, there are greater requirements for staff and technology. So this benefit is provided by IaaS providers, although it seems expensive.
2. Flexibility – IaaS helps in scaling up resources quickly and flexibly as per demand makes. Resources are recovered when they are not in use to save money.
3. Rapid Innovation – During the launch of a new product, computing infrastructure can be built in days or Can be ready within minutes or hours instead of weeks.
4. Helps in Integrating Business (Business Integration) – IaaS helps the workers of the organization Helps focus on business and eliminates infrastructure responsibilities.
5. Better Compatibility – Easy to maintain and upgrade software and hardware or There is no need to troubleshoot as there are very few compatibility issues with it.
6. Secure – Stored data is secured because snapshots of the data are stored in multiple locations. So if a disaster occurs the data can be recovered from other locations. Moreover, the data is secure and can be accessed only by the allotted authorities.
7. Reduce time and cost – The customer is burden free as the hardware maintenance and management service is provided by the company. This also saves overall cost and time.
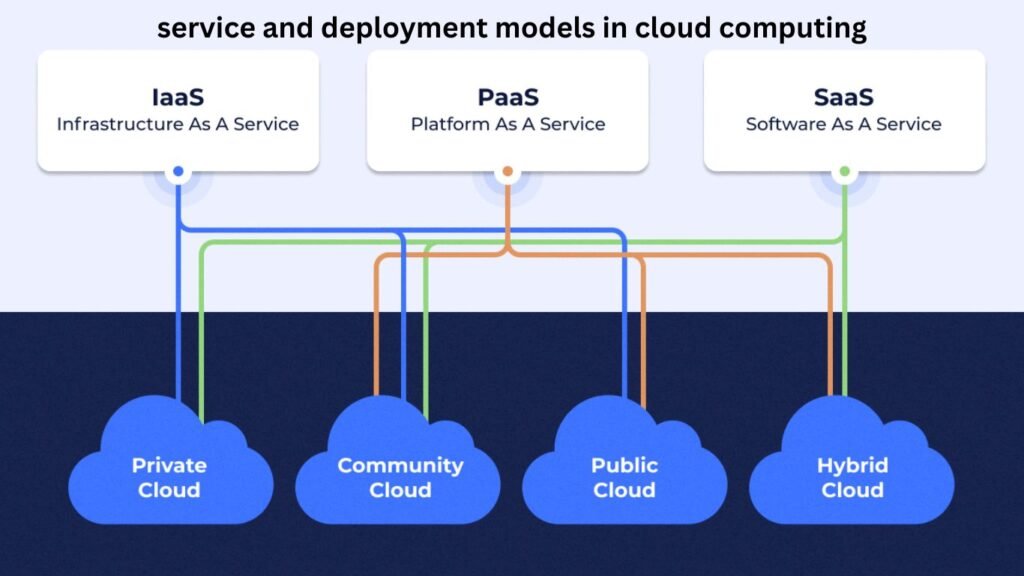
deployment models of Cloud Computing
The deployment models of Cloud Computing are classified on the basis of their location. To know which deployment model will suit your organization’s needs, learn about the types of cloud deployment models as shown in the figure-
1. Private Cloud Computing – An example of private cloud is Google Drive, where all your documents are protected by your e-mail ID and password, no one else can use them except you. This is considered safer to some extent.
2. Public Cloud Computing – Public Cloud is available to every common person; For example, if an eBook is made available for free download on a site and you are able to download it in a single click without creating an account. Public cloud is considered slightly less secure.
3. Community Cloud Computing – Community Cloud Computing is available only to the members of a group, apart from this no other outsider can use this data. For example, only employees of a company can use the data available on that company’s site, or a website created by a school and the content available on it can be used only by the students of that school or institution.
4. Hybrid Cloud Computing – Hybrid cloud includes public cloud and
Private clouds are both used. If some content on a site is publicly available and some content is available only to registered users, such a cloud is called hybrid cloud.
Thanks reading my blog please leave me comments.
