history of Russia
1.Early History: The earliest known Slavic settlements in what is now Russia date back to the 9th century AD. These early Slavic tribes were eventually united under the rule of the Kievan Rus’, a federation of East Slavic tribes centered around the city of Kiev (in present-day Ukraine). The Kievan Rus’ reached its peak during the reign of Prince Vladimir the Great in the 10th century, when Orthodox Christianity was adopted as the state religion.
2.Mongol Rule: In the 13th century, the Mongol Empire, led by Genghis Khan’s successors, swept across Eurasia, including Russia. The Mongols invaded and occupied the Kievan Rus’ territories, establishing the Golden Horde, a Mongol khanate that ruled over much of present-day Russia for over two centuries. This period, known as the Mongol Yoke, profoundly influenced Russian society and governance.
3.Rise of Moscow: Amidst the fragmentation of the Kievan Rus’, the principality of Moscow emerged as a regional power in the 14th and 15th centuries under leaders like Ivan III (also known as Ivan the Great). Ivan III liberated Moscow from Mongol rule and expanded its territory, laying the foundation for the centralized Russian state.
4.Tsardom of Russia: The 16th century saw the consolidation of power under the Grand Duchy of Moscow, which transformed into the Tsardom of Russia in 1547 when Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible) was crowned the first Tsar of Russia. The subsequent centuries witnessed territorial expansion, administrative reforms, and cultural flourishing under the Romanov dynasty, which ruled Russia from 1613 to 1917.
5.Imperial Russia:Russia continued to expand its territory under Peter the Great, Catherine the Great, and other Romanov rulers, becoming the largest contiguous empire in history. The 18th and 19th centuries saw significant social, economic, and political changes, including the Westernization efforts of Peter the Great, the partitions of Poland, and the abolition of serfdom by Tsar Alexander II in 1861.
6.Revolution and Soviet Era:The Russian Revolution of 1917, led by the Bolsheviks under Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Romanov monarchy and established the Soviet Union. Under Bolshevik rule, Russia underwent radical social, economic, and political transformation, including the nationalization of industry, collectivization of agriculture, and the establishment of a one-party state.
7.Post-Soviet Era:The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the emergence of the Russian Federation as an independent state. Russia faced significant challenges in transitioning to a market economy and democratic governance, amidst political upheaval, economic instability, and social change. Vladimir Putin emerged as a dominant political figure, serving as president or prime minister for much of the post-Soviet period, overseeing Russia’s reassertion of influence on the global stage.

Russia, officially known as the Russian Federation, is the largest country in the world by land area, spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. Here are some key points about Russia:
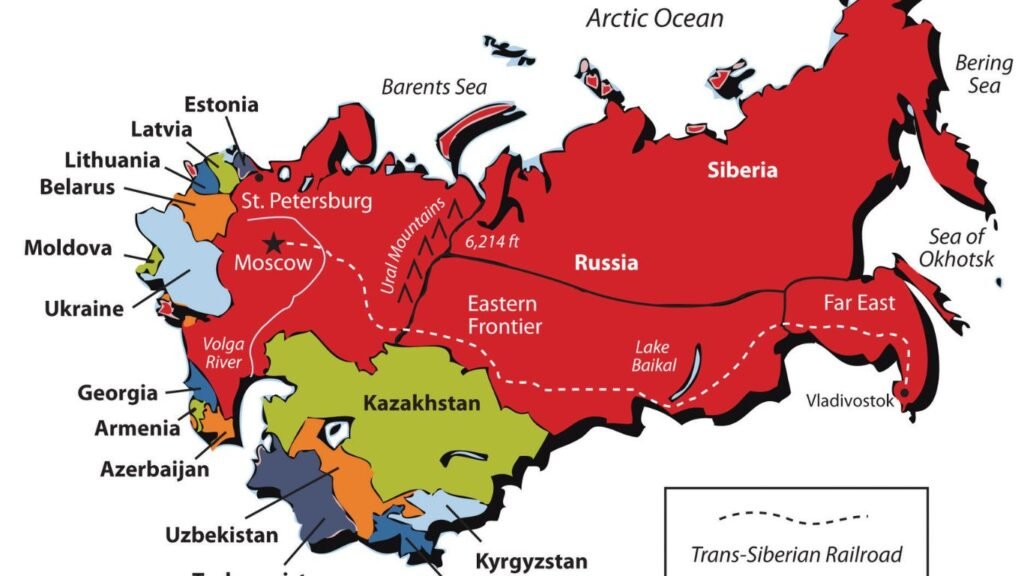
1. Geography: Russia is incredibly vast, covering an area of over 17 million square kilometers. It borders a diverse range of countries, including Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia, and North Korea. The country is known for its diverse landscapes, including the expansive Siberian wilderness, the Ural Mountains, numerous rivers, and the vast Russian Arctic.
2. Population: With a population of over 145 million people, Russia is one of the most populous countries globally. However, its population density is relatively low due to its immense size.
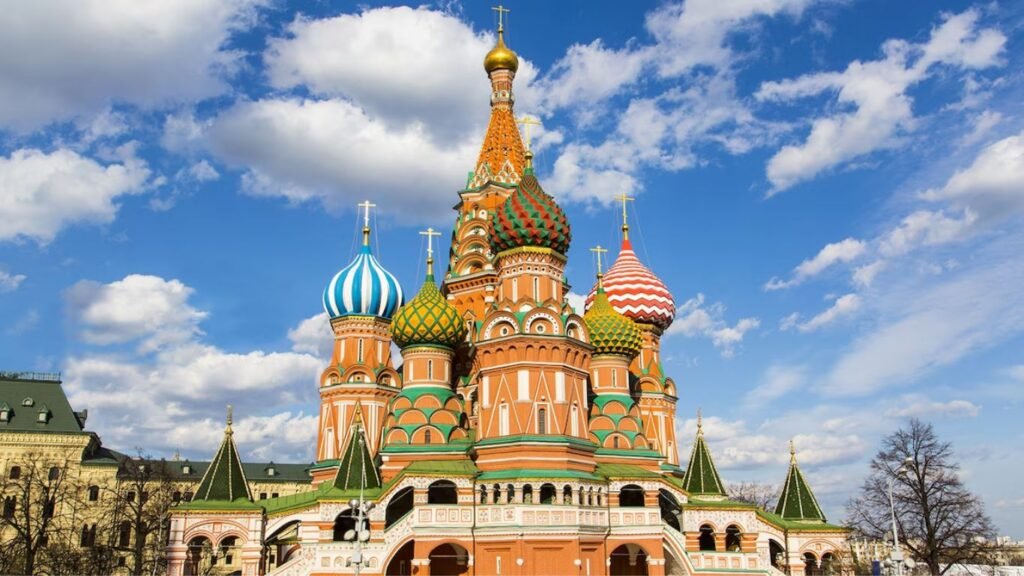
3.Capital and Major Cities: The capital of Russia is Moscow, one of the largest cities in Europe and a major political, economic, cultural, and scientific center. Other major cities include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, and Nizhny Novgorod.
4.Culture:Russian culture is diverse and influenced by its vast geography, history, and various ethnic groups. It has made significant contributions to literature, music, ballet, architecture, cinema, and science. Some of the world’s most renowned authors, composers, and artists, such as Leo Tolstoy, Fyodor Dostoevsky, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky, and Wassily Kandinsky, hail from Russia.
5.Economy:Russia has a mixed economy with vast natural resources, including oil, natural gas, minerals, and timber, which contribute significantly to its GDP. It is one of the world’s leading producers of energy. However, the Russian economy faces challenges such as corruption, economic sanctions, and dependence on natural resources.
6.Politics: Russia is a federal semi-presidential republic with a president as the head of state and a prime minister as the head of government. The political system has been dominated by President Vladimir Putin’s United Russia party since the early 2000s. Russia’s political landscape has been marked by a centralized government, restricted political competition, and concerns about human rights and freedom of expression.
Overall, Russia remains a key player on the global stage due to its geopolitical significance, military power, and vast natural resources.

thanks for reading my blog thanks again.
